Google Sheets Functions
Here's a searchable and sortable table with all 494 Google Sheets functions:
| A | B | C | |
| 1 | Function | Description | Type |
| 2 | =DATE(year, month, day) | Converts a provided year, month, and day into a date. Learn more. | Date |
| 3 | =DATEDIF(start_date, end_date, unit) | Calculates the number of days, months, or years between two dates. Learn more. | Date |
| 4 | =DATEVALUE(date_string) | Converts a provided date string in a known format to a date value. Learn more. | Date |
| 5 | =DAY(date) | Returns the day of the month that a specific date falls on, in numeric format. Learn more. | Date |
| 6 | =DAYS(end_date, start_date) | Returns the number of days between two dates. Learn more. | Date |
| 7 | =DAYS360(start_date, end_date, [method]) | Returns the difference between two days based on the 360 day year used in some financial interest calculations. Learn more. | Date |
| 8 | =EDATE(start_date, months) | Returns a date a specified number of months before or after another date. Learn more. | Date |
| 9 | =EOMONTH(start_date, months) | Returns a date representing the last day of a month which falls a specified number of months before or after another date. Learn more. | Date |
| 10 | =HOUR(time) | Returns the hour component of a specific time, in numeric format. Learn more. | Date |
| 11 | =ISOWEEKNUM(date) | Returns the number of the ISO week of the year where the provided date falls. Learn more. | Date |
| 12 | =MINUTE(time) | Returns the minute component of a specific time, in numeric format. Learn more. | Date |
| 13 | =MONTH(date) | Returns the month of the year a specific date falls in, in numeric format. Learn more. | Date |
| 14 | =NETWORKDAYS(start_date, end_date, [holidays]) | Returns the number of net working days between two provided days. Learn more. | Date |
| 15 | =NETWORKDAYS.INTL(start_date, end_date, [weekend], [holidays]) | Returns the number of net working days between two provided days excluding specified weekend days and holidays. Learn more. | Date |
| 16 | =NOW() | Returns the current date and time as a date value. Learn more. | Date |
| 17 | =SECOND(time) | Returns the second component of a specific time, in numeric format. Learn more. | Date |
| 18 | =TIME(hour, minute, second) | Converts a provided hour, minute, and second into a time. Learn more. | Date |
| 19 | =TIMEVALUE(time_string) | Returns the fraction of a 24-hour day the time represents. Learn more. | Date |
| 20 | =TODAY() | Returns the current date as a date value. Learn more. | Date |
| 21 | =WEEKDAY(date, [type]) | Returns a number representing the day of the week of the date provided. Learn more. | Date |
| 22 | =WEEKNUM(date, [type]) | Returns a number representing the week of the year where the provided date falls. Learn more. | Date |
| 23 | =WORKDAY(start_date, num_days, [holidays]) | Calculates the end date after a specified number of working days. Learn more. | Date |
| 24 | =WORKDAY.INTL(start_date, num_days, [weekend], [holidays]) | Calculates the date after a specified number of workdays excluding specified weekend days and holidays. Learn more. | Date |
| 25 | =YEAR(date) | Returns the year specified by a given date. Learn more. | Date |
| 26 | =YEARFRAC(start_date, end_date, [day_count_convention]) | Returns the number of years, including fractional years, between two dates using a specified day count convention. Learn more. | Date |
| 27 | =BIN2DEC(signed_binary_number) | Converts a signed binary number to decimal format. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 28 | =BIN2HEX(signed_binary_number, [significant_digits]) | Converts a signed binary number to signed hexadecimal format. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 29 | =BIN2OCT(signed_binary_number, [significant_digits]) | Converts a signed binary number to signed octal format. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 30 | =BITAND(value1, value2) | Bitwise boolean AND of two numbers. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 31 | =BITLSHIFT(value, shift_amount) | Shifts the bits of the input a certain number of places to the left. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 32 | =BITOR(value1, value2) | Bitwise boolean OR of 2 numbers. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 33 | =BITRSHIFT(value, shift_amount) | Shifts the bits of the input a certain number of places to the right. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 34 | =BITXOR(value1, value2) | Bitwise XOR (exclusive OR) of 2 numbers. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 35 | =COMPLEX(real_part, imaginary_part, [suffix]) | Creates a complex number given real and imaginary coefficients. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 36 | =DEC2BIN(decimal_number, [significant_digits]) | Converts a decimal number to signed binary format. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 37 | =DEC2HEX(decimal_number, [significant_digits]) | Converts a decimal number to signed hexadecimal format. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 38 | =DEC2OCT(decimal_number, [significant_digits]) | Converts a decimal number to signed octal format. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 39 | =DELTA(number1, [number2]) | Compare two numeric values, returning 1 if they're equal. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 40 | =ERF(lower_bound, [upper_bound]) | The ERF function returns the integral of the Gauss error function over an interval of values. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 41 | =ERF.PRECISE(lower_bound, [upper_bound]) | See ERF. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 42 | =GESTEP(value, [step]) | Returns 1 if the rate is strictly greater than or equal to the provided step value or 0 otherwise. If no step value is provided then the default value of 0 will be used. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 43 | =HEX2BIN(signed_hexadecimal_number, [significant_digits]) | Converts a signed hexadecimal number to signed binary format. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 44 | =HEX2DEC(signed_hexadecimal_number) | Converts a signed hexadecimal number to decimal format. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 45 | =HEX2OCT(signed_hexadecimal_number, significant_digits) | Converts a signed hexadecimal number to signed octal format. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 46 | =IMABS(number) | Returns absolute value of a complex number. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 47 | =IMAGINARY(complex_number) | Returns the imaginary coefficient of a complex number. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 48 | =IMARGUMENT(number) | The IMARGUMENT function returns the angle (also known as the argument or \theta) of the given complex number in radians. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 49 | =IMCONJUGATE(number) | Returns the complex conjugate of a number. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 50 | =IMCOS(number) | The IMCOS function returns the cosine of the given complex number. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 51 | =IMCOSH(number) | Returns the hyperbolic cosine of the given complex number. For example, a given complex number 'x+yi' returns 'cosh(x+yi).'. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 52 | =IMCOT(number) | Returns the cotangent of the given complex number. For example, a given complex number 'x+yi' returns 'cot(x+yi).'. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 53 | =IMCOTH(number) | Returns the hyperbolic cotangent of the given complex number. For example, a given complex number 'x+yi' returns 'coth(x+yi).'. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 54 | =IMCSC(number) | Returns the cosecant of the given complex number. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 55 | =IMCSCH(number) | Returns the hyperbolic cosecant of the given complex number. For example, a given complex number 'x+yi' returns 'csch(x+yi).'. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 56 | =IMDIV(dividend, divisor) | Returns one complex number divided by another. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 57 | =IMEXP(exponent) | Returns Euler's number, e (~2.718) raised to a complex power. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 58 | =IMLOG(value, base) | Returns the logarithm of a complex number for a specified base. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 59 | =IMLOG10(value) | Returns the logarithm of a complex number with base 10. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 60 | =IMLOG2(value) | Returns the logarithm of a complex number with base 2. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 61 | =IMPRODUCT(factor1, [factor2, ...]) | Returns the result of multiplying a series of complex numbers together. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 62 | =IMREAL(complex_number) | Returns the real coefficient of a complex number. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 63 | =IMSEC(number) | Returns the secant of the given complex number. For example, a given complex number 'x+yi' returns 'sec(x+yi).'. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 64 | =IMSECH(number) | Returns the hyperbolic secant of the given complex number. For example, a given complex number 'x+yi' returns 'sech(x+yi).'. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 65 | =IMSIN(number) | Returns the sine of the given complex number. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 66 | =IMSINH(number) | Returns the hyperbolic sine of the given complex number. For example, a given complex number 'x+yi' returns 'sinh(x+yi).'. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 67 | =IMSUB(first_number, second_number) | Returns the difference between two complex numbers. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 68 | =IMSUM(value1, [value2, ...]) | Returns the sum of a series of complex numbers. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 69 | =IMTAN(number) | Returns the tangent of the given complex number. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 70 | =IMTANH(number) | Returns the hyperbolic tangent of the given complex number. For example, a given complex number 'x+yi' returns 'tanh(x+yi).'. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 71 | =OCT2BIN(signed_octal_number, [significant_digits]) | Converts a signed octal number to signed binary format. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 72 | =OCT2DEC(signed_octal_number) | Converts a signed octal number to decimal format. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 73 | =OCT2HEX(signed_octal_number, [significant_digits]) | Converts a signed octal number to signed hexadecimal format. Learn more. | Engineering |
| 74 | =FILTER(range, condition1, [condition2]) | Returns a filtered version of the source range, returning only rows or columns which meet the specified conditions. Learn more. | Filter |
| 75 | =SORT(range, sort_column, is_ascending, [sort_column2], [is_ascending2]) | Sorts the rows of a given array or range by the values in one or more columns. Learn more. | Filter |
| 76 | =SORTN(range, [n], [display_ties_mode], [sort_column1, is_ascending1], ...) | Returns the first n items in a data set after performing a sort. Learn more. | Filter |
| 77 | =UNIQUE(range) | Returns unique rows in the provided source range, discarding duplicates. Rows are returned in the order in which they first appear in the source range. Learn more. | Filter |
| 78 | =ACCRINT(issue, first_payment, settlement, rate, redemption, frequency, [day_count_convention]) | Calculates the accrued interest of a security that has periodic payments. Learn more. | Financial |
| 79 | =ACCRINTM(issue, maturity, rate, [redemption], [day_count_convention]) | Calculates the accrued interest of a security that pays interest at maturity. Learn more. | Financial |
| 80 | =AMORLINC(cost, purchase_date, first_period_end, salvage, period, rate, [basis]) | Returns the depreciation for an accounting period, or the prorated depreciation if the asset was purchased in the middle of a period. Learn more. | Financial |
| 81 | =COUPDAYBS(settlement, maturity, frequency, [day_count_convention]) | Calculates the number of days from the first coupon, or interest payment, until settlement. Learn more. | Financial |
| 82 | =COUPDAYS(settlement, maturity, frequency, [day_count_convention]) | Calculates the number of days in the coupon, or interest payment, period that contains the specified settlement date. Learn more. | Financial |
| 83 | =COUPDAYSNC(settlement, maturity, frequency, [day_count_convention]) | Calculates the number of days from the settlement date until the next coupon, or interest payment. Learn more. | Financial |
| 84 | =COUPNCD(settlement, maturity, frequency, [day_count_convention]) | Calculates next coupon, or interest payment, date after the settlement date. Learn more. | Financial |
| 85 | =COUPNUM(settlement, maturity, frequency, [day_count_convention]) | Calculates the number of coupons, or interest payments, between the settlement date and the maturity date of the investment. Learn more. | Financial |
| 86 | =COUPPCD(settlement, maturity, frequency, [day_count_convention]) | Calculates last coupon, or interest payment, date before the settlement date. Learn more. | Financial |
| 87 | =CUMIPMT(rate, number_of_periods, present_value, first_period, last_period, end_or_beginning) | Calculates the cumulative interest over a range of payment periods for an investment based on constant-amount periodic payments and a constant interest rate. Learn more. | Financial |
| 88 | =CUMPRINC(rate, number_of_periods, present_value, first_period, last_period, end_or_beginning) | Calculates the cumulative principal paid over a range of payment periods for an investment based on constant-amount periodic payments and a constant interest rate. Learn more. | Financial |
| 89 | =DB(cost, salvage, life, period, [month]) | Calculates the depreciation of an asset for a specified period using the arithmetic declining balance method. Learn more. | Financial |
| 90 | =DDB(cost, salvage, life, period, [factor]) | Calculates the depreciation of an asset for a specified period using the double-declining balance method. Learn more. | Financial |
| 91 | =DISC(settlement, maturity, price, redemption, [day_count_convention]) | Calculates the discount rate of a security based on price. Learn more. | Financial |
| 92 | =DOLLARDE(fractional_price, unit) | Converts a price quotation given as a decimal fraction into a decimal value. Learn more. | Financial |
| 93 | =DOLLARFR(decimal_price, unit) | Converts a price quotation given as a decimal value into a decimal fraction. Learn more. | Financial |
| 94 | =DURATION(settlement, maturity, rate, yield, frequency, [day_count_convention]) | Calculates the number of compounding periods required for an investment of a specified present value appreciating at a given rate to reach a target value. Learn more. | Financial |
| 95 | =EFFECT(nominal_rate, periods_per_year) | Calculates the annual effective interest rate given the nominal rate and number of compounding periods per year. Learn more. | Financial |
| 96 | =FV(rate, number_of_periods, payment_amount, [present_value], [end_or_beginning]) | Calculates the future value of an annuity investment based on constant-amount periodic payments and a constant interest rate. Learn more. | Financial |
| 97 | =FVSCHEDULE(principal, rate_schedule) | Calculates the future value of some principal based on a specified series of potentially varying interest rates. Learn more. | Financial |
| 98 | =INTRATE(buy_date, sell_date, buy_price, sell_price, [day_count_convention]) | Calculates the effective interest rate generated when an investment is purchased at one price and sold at another with no interest or dividends generated by the investment itself. Learn more. | Financial |
| 99 | =IPMT(rate, period, number_of_periods, present_value, [future_value], [end_or_beginning]) | Calculates the payment on interest for an investment based on constant-amount periodic payments and a constant interest rate. Learn more. | Financial |
| 100 | =IRR(cashflow_amounts, [rate_guess]) | Calculates the internal rate of return on an investment based on a series of periodic cash flows. Learn more. | Financial |
| 101 | =ISPMT(rate, period, number_of_periods, present_value) | The ISPMT function calculates the interest paid during a particular period of an investment. Learn more. | Financial |
| 102 | =MDURATION(settlement, maturity, rate, yield, frequency, [day_count_convention]) | Calculates the modified Macaulay duration of a security paying periodic interest, such as a US Treasury Bond, based on expected yield. Learn more. | Financial |
| 103 | =MIRR(cashflow_amounts, financing_rate, reinvestment_return_rate) | Calculates the modified internal rate of return on an investment based on a series of periodic cash flows and the difference between the interest rate paid on financing versus the return received on reinvested income. Learn more. | Financial |
| 104 | =NOMINAL(effective_rate, periods_per_year) | Calculates the annual nominal interest rate given the effective rate and number of compounding periods per year. Learn more. | Financial |
| 105 | =NPER(rate, payment_amount, present_value, [future_value], [end_or_beginning]) | Calculates the number of payment periods for an investment based on constant-amount periodic payments and a constant interest rate. Learn more. | Financial |
| 106 | =NPV(discount, cashflow1, [cashflow2, ...]) | Calculates the net present value of an investment based on a series of periodic cash flows and a discount rate. Learn more. | Financial |
| 107 | =PDURATION(rate, present_value, future_value) | Returns the number of periods for an investment to reach a specific value at a given rate. Learn more. | Financial |
| 108 | =PMT(rate, number_of_periods, present_value, [future_value], [end_or_beginning]) | Calculates the periodic payment for an annuity investment based on constant-amount periodic payments and a constant interest rate. Learn more. | Financial |
| 109 | =PPMT(rate, period, number_of_periods, present_value, [future_value], [end_or_beginning]) | Calculates the payment on the principal of an investment based on constant-amount periodic payments and a constant interest rate. Learn more. | Financial |
| 110 | =PRICE(settlement, maturity, rate, yield, redemption, frequency, [day_count_convention]) | Calculates the price of a security paying periodic interest, such as a US Treasury Bond, based on expected yield. Learn more. | Financial |
| 111 | =PRICEDISC(settlement, maturity, discount, redemption, [day_count_convention]) | Calculates the price of a discount (non-interest-bearing) security, based on expected yield. Learn more. | Financial |
| 112 | =PRICEMAT(settlement, maturity, issue, rate, yield, [day_count_convention]) | Calculates the price of a security paying interest at maturity, based on expected yield. Learn more. | Financial |
| 113 | =PV(rate, number_of_periods, payment_amount, [future_value], [end_or_beginning]) | Calculates the present value of an annuity investment based on constant-amount periodic payments and a constant interest rate. Learn more. | Financial |
| 114 | =RATE(number_of_periods, payment_per_period, present_value, [future_value], [end_or_beginning], [rate_guess]) | Calculates the interest rate of an annuity investment based on constant-amount periodic payments and the assumption of a constant interest rate. Learn more. | Financial |
| 115 | =RECEIVED(settlement, maturity, investment, discount, [day_count_convention]) | Calculates the amount received at maturity for an investment in fixed-income securities purchased on a given date. Learn more. | Financial |
| 116 | =RRI(number_of_periods, present_value, future_value) | Returns the interest rate needed for an investment to reach a specific value within a given number of periods. Learn more. | Financial |
| 117 | =SLN(cost, salvage, life) | Calculates the depreciation of an asset for one period using the straight-line method. Learn more. | Financial |
| 118 | =SYD(cost, salvage, life, period) | Calculates the depreciation of an asset for a specified period using the sum of years digits method. Learn more. | Financial |
| 119 | =TBILLEQ(settlement, maturity, discount) | Calculates the equivalent annualized rate of return of a US Treasury Bill based on discount rate. Learn more. | Financial |
| 120 | =TBILLPRICE(settlement, maturity, discount) | Calculates the price of a US Treasury Bill based on discount rate. Learn more. | Financial |
| 121 | =TBILLYIELD(settlement, maturity, price) | Calculates the yield of a US Treasury Bill based on price. Learn more. | Financial |
| 122 | =VDB(cost, salvage, life, start_period, end_period, [factor], [no_switch]) | Returns the depreciation of an asset for a particular period (or partial period). Learn more. | Financial |
| 123 | =XIRR(cashflow_amounts, cashflow_dates, [rate_guess]) | Calculates the internal rate of return of an investment based on a specified series of potentially irregularly spaced cash flows. Learn more. | Financial |
| 124 | =XNPV(discount, cashflow_amounts, cashflow_dates) | Calculates the net present value of an investment based on a specified series of potentially irregularly spaced cash flows and a discount rate. Learn more. | Financial |
| 125 | =YIELD(settlement, maturity, rate, price, redemption, frequency, [day_count_convention]) | Calculates the annual yield of a security paying periodic interest, such as a US Treasury Bond, based on price. Learn more. | Financial |
| 126 | =YIELDDISC(settlement, maturity, price, redemption, [day_count_convention]) | Calculates the annual yield of a discount (non-interest-bearing) security, based on price. Learn more. | Financial |
| 127 | =YIELDMAT(settlement, maturity, issue, rate, price, [day_count_convention]) | Calculates the annual yield of a security paying interest at maturity, based on price. Learn more. | Financial |
| 128 | =ARRAYFORMULA(array_formula) | Enables the display of values returned from an array formula into multiple rows and/or columns and the use of non-array functions with arrays. Learn more. | |
| 129 | =DETECTLANGUAGE(text_or_range) | Identifies the language used in text within the specified range. Learn more. | |
| 130 | =GOOGLEFINANCE(ticker, [attribute], [start_date], [end_date|num_days], [interval]) | Fetches current or historical securities information from Google Finance. Learn more. | |
| 131 | =GOOGLETRANSLATE(text, [source_language], [target_language]) | Translates text from one language into another. Learn more. | |
| 132 | =IMAGE(url, [mode], [height], [width]) | Inserts an image into a cell. Learn more. | |
| 133 | =QUERY(data, query, [headers]) | Runs a Google Visualization API Query Language query across data. Learn more. | |
| 134 | =SPARKLINE(data, [options]) | Creates a miniature chart contained within a single cell. Learn more. | |
| 135 | =ERROR.TYPE(reference) | Returns a number corresponding to the error value in a different cell. Learn more. | Info |
| 136 | =ISBLANK(value) | Checks whether the referenced cell is empty. Learn more. | Info |
| 137 | =ISDATE(value) | Returns whether a value is a date. Learn more. | Info |
| 138 | =ISEMAIL(value) | Checks whether a value is a valid email address. Learn more. | Info |
| 139 | =ISERR(value) | Checks whether a value is an error other than `#N/A`. Learn more. | Info |
| 140 | =ISERROR(value) | Checks whether a value is an error. Learn more. | Info |
| 141 | =ISFORMULA(cell) | Checks whether a formula is in the referenced cell. Learn more. | Info |
| 142 | =ISLOGICAL(value) | Checks whether a value is `TRUE` or `FALSE`. Learn more. | Info |
| 143 | =ISNA(value) | Checks whether a value is the error `#N/A`. Learn more. | Info |
| 144 | =ISNONTEXT(value) | Checks whether a value is non-textual. Learn more. | Info |
| 145 | =ISNUMBER(value) | Checks whether a value is a number. Learn more. | Info |
| 146 | =ISREF(value) | Checks whether a value is a valid cell reference. Learn more. | Info |
| 147 | =ISTEXT(value) | Checks whether a value is text. Learn more. | Info |
| 148 | =N(value) | Returns the argument provided as a number. Learn more. | Info |
| 149 | =NA() | Returns the 'value not available' error, `#N/A`. Learn more. | Info |
| 150 | =TYPE(value) | Returns a number associated with the type of data passed into the function. Learn more. | Info |
| 151 | =CELL(info_type, reference) | Returns the requested information about the specified cell. Learn more. | Info |
| 152 | =AND(logical_expression1, [logical_expression2, ...]) | Returns true if all of the provided arguments are logically true, and false if any of the provided arguments are logically false. Learn more. | Logical |
| 153 | =FALSE() | Returns the logical value `FALSE`. Learn more. | Logical |
| 154 | =IF(logical_expression, value_if_true, value_if_false) | Returns one value if a logical expression is `TRUE` and another if it is `FALSE`. Learn more. | Logical |
| 155 | =IFERROR(value, [value_if_error]) | Returns the first argument if it is not an error value, otherwise returns the second argument if present, or a blank if the second argument is absent. Learn more. | Logical |
| 156 | =IFNA(value, value_if_na) | Evaluates a value. If the value is an #N/A error, returns the specified value. Learn more. | Logical |
| 157 | =IFS(condition1, value1, [condition2, value2], …) | Evaluates multiple conditions and returns a value that corresponds to the first true condition. Learn more. | Logical |
| 158 | =NOT(logical_expression) | Returns the opposite of a logical value - `NOT(TRUE)` returns `FALSE`; `NOT(FALSE)` returns `TRUE`. Learn more. | Logical |
| 159 | =OR(logical_expression1, [logical_expression2, ...]) | Returns true if any of the provided arguments are logically true, and false if all of the provided arguments are logically false. Learn more. | Logical |
| 160 | =SWITCH(expression, case1, value1, [default or case2, value2], …) | Tests an expression against a list of cases and returns the corresponding value of the first matching case, with an optional default value if nothing else is met. Learn more. | Logical |
| 161 | =TRUE() | Returns the logical value `TRUE`. Learn more. | Logical |
| 162 | =XOR(logical_expression1, [logical_expression2, ...]) | The XOR function performs an exclusive or of 2 numbers that returns a 1 if the numbers are different, and a 0 otherwise. Learn more. | Logical |
| 163 | =ADDRESS(row, column, [absolute_relative_mode], [use_a1_notation], [sheet]) | Returns a cell reference as a string. Learn more. | Lookup |
| 164 | =CHOOSE(index, choice1, [choice2, ...]) | Returns an element from a list of choices based on index. Learn more. | Lookup |
| 165 | =COLUMN([cell_reference]) | Returns the column number of a specified cell, with `A=1`. Learn more. | Lookup |
| 166 | =COLUMNS(range) | Returns the number of columns in a specified array or range. Learn more. | Lookup |
| 167 | =FORMULATEXT(cell) | Returns the formula as a string. Learn more. | Lookup |
| 168 | =GETPIVOTDATA(value_name, any_pivot_table_cell, [original_column, ...], [pivot_item, ...]) | Extracts an aggregated value from a pivot table that corresponds to the specified row and column headings. Learn more. | Lookup |
| 169 | =HLOOKUP(search_key, range, index, [is_sorted]) | Horizontal lookup. Searches across the first row of a range for a key and returns the value of a specified cell in the column found. Learn more. | Lookup |
| 170 | =INDEX(reference, [row], [column]) | Returns the content of a cell, specified by row and column offset. Learn more. | Lookup |
| 171 | =INDIRECT(cell_reference_as_string, [is_A1_notation]) | Returns a cell reference specified by a string. Learn more. | Lookup |
| 172 | =LOOKUP(search_key, search_range|search_result_array, [result_range]) | Looks through a row or column for a key and returns the value of the cell in a result range located in the same position as the search row or column. Learn more. | Lookup |
| 173 | =MATCH(search_key, range, [search_type]) | Returns the relative position of an item in a range that matches a specified value. Learn more. | Lookup |
| 174 | =OFFSET(cell_reference, offset_rows, offset_columns, [height], [width]) | Returns a range reference shifted a specified number of rows and columns from a starting cell reference. Learn more. | Lookup |
| 175 | =ROW([cell_reference]) | Returns the row number of a specified cell. Learn more. | Lookup |
| 176 | =ROWS(range) | Returns the number of rows in a specified array or range. Learn more. | Lookup |
| 177 | =VLOOKUP(search_key, range, index, [is_sorted]) | Vertical lookup. Searches down the first column of a range for a key and returns the value of a specified cell in the row found. Learn more. | Lookup |
| 178 | =ABS(value) | Returns the absolute value of a number. Learn more. | Math |
| 179 | =ACOS(value) | Returns the inverse cosine of a value, in radians. Learn more. | Math |
| 180 | =ACOSH(value) | Returns the inverse hyperbolic cosine of a number. Learn more. | Math |
| 181 | =ACOT(value) | Returns the inverse cotangent of a value, in radians. Learn more. | Math |
| 182 | =ACOTH(value) | Returns the inverse hyperbolic cotangent of a value, in radians. Must not be between -1 and 1, inclusive. Learn more. | Math |
| 183 | =ASIN(value) | Returns the inverse sine of a value, in radians. Learn more. | Math |
| 184 | =ASINH(value) | Returns the inverse hyperbolic sine of a number. Learn more. | Math |
| 185 | =ATAN(value) | Returns the inverse tangent of a value, in radians. Learn more. | Math |
| 186 | =ATAN2(x, y) | Returns the angle between the x-axis and a line segment from the origin (0,0) to specified coordinate pair (`x`,`y`), in radians. Learn more. | Math |
| 187 | =ATANH(value) | Returns the inverse hyperbolic tangent of a number. Learn more. | Math |
| 188 | =BASE(value, base, [min_length]) | Converts a number into a text representation in another base, for example, base 2 for binary. Learn more. | Math |
| 189 | =CEILING(value, [factor]) | Rounds a number up to the nearest integer multiple of specified significance. Learn more. | Math |
| 190 | =CEILING.MATH(number, [significance], [mode]) | Rounds a number up to the nearest integer multiple of specified significance, with negative numbers rounding toward or away from 0 depending on the mode. Learn more. | Math |
| 191 | =CEILING.PRECISE(number, [significance]) | Rounds a number up to the nearest integer multiple of specified significance. If the number is positive or negative, it is rounded up. Learn more. | Math |
| 192 | =COMBIN(n, k) | Returns the number of ways to choose some number of objects from a pool of a given size of objects. Learn more. | Math |
| 193 | =COMBINA(n, k) | Returns the number of ways to choose some number of objects from a pool of a given size of objects, including ways that choose the same object multiple times. Learn more. | Math |
| 194 | =COS(angle) | Returns the cosine of an angle provided in radians. Learn more. | Math |
| 195 | =COSH(value) | Returns the hyperbolic cosine of any real number. Learn more. | Math |
| 196 | =COT(angle) | Cotangent of an angle provided in radians. Learn more. | Math |
| 197 | =COTH(value) | Returns the hyperbolic cotangent of any real number. Learn more. | Math |
| 198 | =COUNTBLANK(range) | Returns the number of empty cells in a given range. Learn more. | Math |
| 199 | =COUNTIF(range, criterion) | Returns a conditional count across a range. Learn more. | Math |
| 200 | =COUNTIFS(criteria_range1, criterion1, [criteria_range2, criterion2, ...]) | Returns the count of a range depending on multiple criteria. Learn more. | Math |
| 201 | =COUNTUNIQUE(value1, [value2, ...]) | Counts the number of unique values in a list of specified values and ranges. Learn more. | Math |
| 202 | =CSC(angle) | Returns the cosecant of an angle provided in radians. Learn more. | Math |
| 203 | =CSCH(value) | The CSCH function returns the hyperbolic cosecant of any real number. Learn more. | Math |
| 204 | =DECIMAL(value, base) | The DECIMAL function converts the text representation of a number in another base, to base 10 (decimal). Learn more. | Math |
| 205 | =DEGREES(angle) | Converts an angle value in radians to degrees. Learn more. | Math |
| 206 | =ERFC(z) | Returns the complementary Gauss error function of a value. Learn more. | Math |
| 207 | =ERFC.PRECISE(z) | See ERFC. Learn more. | Math |
| 208 | =EVEN(value) | Rounds a number up to the nearest even integer. Learn more. | Math |
| 209 | =EXP(exponent) | Returns Euler's number, e (~2.718) raised to a power. Learn more. | Math |
| 210 | =FACT(value) | Returns the factorial of a number. Learn more. | Math |
| 211 | =FACTDOUBLE(value) | Returns the 'double factorial' of a number. Learn more. | Math |
| 212 | =FLOOR(value, [factor]) | Rounds a number down to the nearest integer multiple of specified significance. Learn more. | Math |
| 213 | =FLOOR.MATH(number, [significance], [mode]) | Rounds a number down to the nearest integer multiple of specified significance, with negative numbers rounding toward or away from 0 depending on the mode. Learn more. | Math |
| 214 | =FLOOR.PRECISE(number, [significance]) | The FLOOR.PRECISE function rounds a number down to the nearest integer or multiple of specified significance. Learn more. | Math |
| 215 | =GAMMALN(value) | Returns the the logarithm of a specified Gamma function, base e (Euler's number). Learn more. | Math |
| 216 | =GAMMALN.PRECISE(value) | See GAMMALN. Learn more. | Math |
| 217 | =GCD(value1, value2) | Returns the greatest common divisor of one or more integers. Learn more. | Math |
| 218 | =IMLN(complex_value) | Returns the logarithm of a complex number, base e (Euler's number). Learn more. | Math |
| 219 | =IMPOWER(complex_base, exponent) | Returns a complex number raised to a power. Learn more. | Math |
| 220 | =IMSQRT(complex_number) | Computes the square root of a complex number. Learn more. | Math |
| 221 | =INT(value) | Rounds a number down to the nearest integer that is less than or equal to it. Learn more. | Math |
| 222 | =ISEVEN(value) | Checks whether the provided value is even. Learn more. | Math |
| 223 | =ISO.CEILING(number, [significance]) | See CEILING.PRECISE. Learn more. | Math |
| 224 | =ISODD(value) | Checks whether the provided value is odd. Learn more. | Math |
| 225 | =LCM(value1, value2) | Returns the least common multiple of one or more integers. Learn more. | Math |
| 226 | =LN(value) | Returns the the logarithm of a number, base e (Euler's number). Learn more. | Math |
| 227 | =LOG(value, base) | Returns the the logarithm of a number given a base. Learn more. | Math |
| 228 | =LOG10(value) | Returns the the logarithm of a number, base 10. Learn more. | Math |
| 229 | =MOD(dividend, divisor) | Returns the result of the modulo operator, the remainder after a division operation. Learn more. | Math |
| 230 | =MROUND(value, factor) | Rounds one number to the nearest integer multiple of another. Learn more. | Math |
| 231 | =MULTINOMIAL(value1, value2) | Returns the factorial of the sum of values divided by the product of the values' factorials. Learn more. | Math |
| 232 | =MUNIT(dimension) | Returns a unit matrix of size dimension x dimension. Learn more. | Math |
| 233 | =ODD(value) | Rounds a number up to the nearest odd integer. Learn more. | Math |
| 234 | =PI() | Returns the value of Pi to 14 decimal places. Learn more. | Math |
| 235 | =POWER(base, exponent) | Returns a number raised to a power. Learn more. | Math |
| 236 | =PRODUCT(factor1, [factor2, ...]) | Returns the result of multiplying a series of numbers together. Learn more. | Math |
| 237 | =QUOTIENT(dividend, divisor) | Returns one number divided by another. Learn more. | Math |
| 238 | =RADIANS(angle) | Converts an angle value in degrees to radians. Learn more. | Math |
| 239 | =RAND() | Returns a random number between 0 inclusive and 1 exclusive. Learn more. | Math |
| 240 | =RANDARRAY(rows, columns) | Generates an array of random numbers between 0 and 1. Learn more. | Math |
| 241 | =RANDBETWEEN(low, high) | Returns a uniformly random integer between two values, inclusive. Learn more. | Math |
| 242 | =ROUND(value, [places]) | Rounds a number to a certain number of decimal places according to standard rules. Learn more. | Math |
| 243 | =ROUNDDOWN(value, [places]) | Rounds a number to a certain number of decimal places, always rounding down to the next valid increment. Learn more. | Math |
| 244 | =ROUNDUP(value, [places]) | Rounds a number to a certain number of decimal places, always rounding up to the next valid increment. Learn more. | Math |
| 245 | =SEC(angle) | The SEC function returns the secant of an angle, measured in radians. Learn more. | Math |
| 246 | =SECH(value) | The SECH function returns the hyperbolic secant of an angle. Learn more. | Math |
| 247 | =SEQUENCE(rows, columns, start, step) | Returns an array of sequential numbers, such as 1, 2, 3, 4. Learn more. | Math |
| 248 | =SERIESSUM(x, n, m, a) | Given parameters x, n, m, and a, returns the power series sum a1xn + a2x(n+m) + ... + aix(n+(i-1)m), where i is the number of entries in range `a`. Learn more. | Math |
| 249 | =SIGN(value) | Given an input number, returns `-1` if it is negative, `1` if positive, and `0` if it is zero. Learn more. | Math |
| 250 | =SIN(angle) | Returns the sine of an angle provided in radians. Learn more. | Math |
| 251 | =SINH(value) | Returns the hyperbolic sine of any real number. Learn more. | Math |
| 252 | =SQRT(value) | Returns the positive square root of a positive number. Learn more. | Math |
| 253 | =SQRTPI(value) | Returns the positive square root of the product of Pi and the given positive number. Learn more. | Math |
| 254 | =SUBTOTAL(function_code, range1, [range2, ...]) | Returns a subtotal for a vertical range of cells using a specified aggregation function. Learn more. | Math |
| 255 | =SUM(value1, [value2, ...]) | Returns the sum of a series of numbers and/or cells. Learn more. | Math |
| 256 | =SUMIF(range, criterion, [sum_range]) | Returns a conditional sum across a range. Learn more. | Math |
| 257 | =SUMIFS(sum_range, criteria_range1, criterion1, [criteria_range2, criterion2, ...]) | Returns the sum of a range depending on multiple criteria. Learn more. | Math |
| 258 | =SUMSQ(value1, [value2, ...]) | Returns the sum of the squares of a series of numbers and/or cells. Learn more. | Math |
| 259 | =TAN(angle) | Returns the tangent of an angle provided in radians. Learn more. | Math |
| 260 | =TANH(value) | Returns the hyperbolic tangent of any real number. Learn more. | Math |
| 261 | =TRUNC(value, [places]) | Truncates a number to a certain number of significant digits by omitting less significant digits. Learn more. | Math |
| 262 | =ADD(value1, value2) | Returns the sum of two numbers. Equivalent to the `+` operator. Learn more. | Operator |
| 263 | =CONCAT(value1, value2) | Returns the concatenation of two values. Equivalent to the `&` operator. Learn more. | Operator |
| 264 | =DIVIDE(dividend, divisor) | Returns one number divided by another. Equivalent to the `/` operator. Learn more. | Operator |
| 265 | =EQ(value1, value2) | Returns `TRUE` if two specified values are equal and `FALSE` otherwise. Equivalent to the `=` operator. Learn more. | Operator |
| 266 | =GT(value1, value2) | Returns `TRUE` if the first argument is strictly greater than the second, and `FALSE` otherwise. Equivalent to the `>` operator. Learn more. | Operator |
| 267 | =GTE(value1, value2) | Returns `TRUE` if the first argument is greater than or equal to the second, and `FALSE` otherwise. Equivalent to the `>=` operator. Learn more. | Operator |
| 268 | =ISBETWEEN(value_to_compare, lower_value, upper_value, lower_value_is_inclusive, upper_value_is_inclusive) | Checks whether a provided number is between two other numbers either inclusively or exclusively. Learn more. | Operator |
| 269 | =LT(value1, value2) | Returns `TRUE` if the first argument is strictly less than the second, and `FALSE` otherwise. Equivalent to the `<` operator. Learn more. | Operator |
| 270 | =LTE(value1, value2) | Returns `TRUE` if the first argument is less than or equal to the second, and `FALSE` otherwise. Equivalent to the `<=` operator. Learn more. | Operator |
| 271 | =MINUS(value1, value2) | Returns the difference of two numbers. Equivalent to the `-` operator. Learn more. | Operator |
| 272 | =MULTIPLY(factor1, factor2) | Returns the product of two numbers. Equivalent to the `*` operator. Learn more. | Operator |
| 273 | =NE(value1, value2) | Returns `TRUE` if two specified values are not equal and `FALSE` otherwise. Equivalent to the `<>` operator. Learn more. | Operator |
| 274 | =POW(base, exponent) | Returns a number raised to a power. Learn more. | Operator |
| 275 | =UMINUS(value) | Returns a number with the sign reversed. Learn more. | Operator |
| 276 | =UNARY_PERCENT(percentage) | Returns a value interpreted as a percentage; that is, `UNARY_PERCENT(100)` equals `1`. Learn more. | Operator |
| 277 | =UNIQUE(range, by_column, exactly_once) | Returns unique rows in the provided source range, discarding duplicates. Rows are returned in the order in which they first appear in the source range. Learn more. | Operator |
| 278 | =UPLUS(value) | Returns a specified number, unchanged. Learn more. | Operator |
| 279 | =AVEDEV(value1, [value2, ...]) | Calculates the average of the magnitudes of deviations of data from a dataset's mean. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 280 | =AVERAGE(value1, [value2, ...]) | Returns the numerical average value in a dataset, ignoring text. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 281 | =AVERAGE.WEIGHTED(values, weights, [additional values], [additional weights]) | Finds the weighted average of a set of values, given the values and the corresponding weights. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 282 | =AVERAGEA(value1, [value2, ...]) | Returns the numerical average value in a dataset. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 283 | =AVERAGEIF(criteria_range, criterion, [average_range]) | Returns the average of a range depending on criteria. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 284 | =AVERAGEIFS(average_range, criteria_range1, criterion1, [criteria_range2, criterion2, ...]) | Returns the average of a range depending on multiple criteria. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 285 | =BETA.DIST(value, alpha, beta, cumulative, lower_bound, upper_bound) | Returns the probability of a given value as defined by the beta distribution function. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 286 | =BETA.INV(probability, alpha, beta, lower_bound, upper_bound) | Returns the value of the inverse beta distribution function for a given probability. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 287 | =BETADIST(value, alpha, beta, lower_bound, upper_bound) | See BETA.DIST. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 288 | =BETAINV(probability, alpha, beta, lower_bound, upper_bound) | See BETA.INV. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 289 | =BINOM.DIST(num_successes, num_trials, prob_success, cumulative) | See BINOMDIST. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 290 | =BINOM.INV(num_trials, prob_success, target_prob) | See CRITBINOM. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 291 | =BINOMDIST(num_successes, num_trials, prob_success, cumulative) | Calculates the probability of drawing a certain number of successes (or a maximum number of successes) in a certain number of tries given a population of a certain size containing a certain number of successes, with replacement of draws. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 292 | =CHIDIST(x, degrees_freedom) | Calculates the right-tailed chi-squared distribution, often used in hypothesis testing. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 293 | =CHIINV(probability, degrees_freedom) | Calculates the inverse of the right-tailed chi-squared distribution. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 294 | =CHISQ.DIST(x, degrees_freedom, cumulative) | Calculates the left-tailed chi-squared distribution, often used in hypothesis testing. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 295 | =CHISQ.DIST.RT(x, degrees_freedom) | Calculates the right-tailed chi-squared distribution, which is commonly used in hypothesis testing. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 296 | =CHISQ.INV(probability, degrees_freedom) | Calculates the inverse of the left-tailed chi-squared distribution. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 297 | =CHISQ.INV.RT(probability, degrees_freedom) | Calculates the inverse of the right-tailed chi-squared distribution. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 298 | =CHISQ.TEST(observed_range, expected_range) | See CHITEST. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 299 | =CHITEST(observed_range, expected_range) | Returns the probability associated with a Pearson’s chi-squared test on the two ranges of data. Determines the likelihood that the observed categorical data is drawn from an expected distribution. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 300 | =CONFIDENCE(alpha, standard_deviation, pop_size) | See CONFIDENCE.NORM. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 301 | =CONFIDENCE.NORM(alpha, standard_deviation, pop_size) | Calculates the width of half the confidence interval for a normal distribution. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 302 | =CONFIDENCE.T(alpha, standard_deviation, size) | Calculates the width of half the confidence interval for a Student’s t-distribution. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 303 | =CORREL(data_y, data_x) | Calculates r, the Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient of a dataset. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 304 | =COUNT(value1, [value2, ...]) | Returns a count of the number of numeric values in a dataset. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 305 | =COUNTA(value1, [value2, ...]) | Returns a count of the number of values in a dataset. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 306 | =COVAR(data_y, data_x) | Calculates the covariance of a dataset. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 307 | =COVARIANCE.P(data_y, data_x) | See COVAR. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 308 | =COVARIANCE.S(data_y, data_x) | Calculates the covariance of a dataset, where the dataset is a sample of the total population. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 309 | =CRITBINOM(num_trials, prob_success, target_prob) | Calculates the smallest value for which the cumulative binomial distribution is greater than or equal to a specified criteria. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 310 | =DEVSQ(value1, value2) | Calculates the sum of squares of deviations based on a sample. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 311 | =EXPON.DIST(x, lambda, cumulative) | Returns the value of the exponential distribution function with a specified lambda at a specified value. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 312 | =EXPONDIST(x, lambda, cumulative) | See EXPON.DIST. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 313 | =F.DIST(x, degrees_freedom1, degrees_freedom2, cumulative) | Calculates the left-tailed F probability distribution (degree of diversity) for two data sets with given input x. Alternately called Fisher-Snedecor distribution or Snedecor's F distribution. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 314 | =F.DIST.RT(x, degrees_freedom1, degrees_freedom2) | Calculates the right-tailed F probability distribution (degree of diversity) for two data sets with given input x. Alternately called Fisher-Snedecor distribution or Snedecor's F distribution. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 315 | =F.INV(probability, degrees_freedom1, degrees_freedom2) | Calculates the inverse of the left-tailed F probability distribution. Also called the Fisher-Snedecor distribution or Snedecor’s F distribution. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 316 | =F.INV.RT(probability, degrees_freedom1, degrees_freedom2) | Calculates the inverse of the right-tailed F probability distribution. Also called the Fisher-Snedecor distribution or Snedecor’s F distribution. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 317 | =F.TEST(range1, range2) | See FTEST. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 318 | =FDIST(x, degrees_freedom1, degrees_freedom2) | See F.DIST.RT. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 319 | =FINV(probability, degrees_freedom1, degrees_freedom2) | See F.INV.RT. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 320 | =FISHER(value) | Returns the Fisher transformation of a specified value. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 321 | =FISHERINV(value) | Returns the inverse Fisher transformation of a specified value. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 322 | =FORECAST(x, data_y, data_x) | Calculates the expected y-value for a specified x based on a linear regression of a dataset. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 323 | =FORECAST.LINEAR(x, data_y, data_x) | See FORECAST. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 324 | =FTEST(range1, range2) | Returns the probability associated with an F-test for equality of variances. Determines whether two samples are likely to have come from populations with the same variance. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 325 | =GAMMA(number) | Returns the Gamma function evaluated at the specified value. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 326 | =GAMMA.DIST(x, alpha, beta, cumulative) | Calculates the gamma distribution, a two-parameter continuous probability distribution. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 327 | =GAMMA.INV(probability, alpha, beta) | The GAMMA.INV function returns the value of the inverse gamma cumulative distribution function for the specified probability and alpha and beta parameters. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 328 | =GAMMADIST(x, alpha, beta, cumulative) | See GAMMA.DIST. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 329 | =GAMMAINV(probability, alpha, beta) | See GAMMA.INV. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 330 | =GAUSS(z) | The GAUSS function returns the probability that a random variable, drawn from a normal distribution, will be between the mean and z standard deviations above (or below) the mean. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 331 | =GEOMEAN(value1, value2) | Calculates the geometric mean of a dataset. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 332 | =HARMEAN(value1, value2) | Calculates the harmonic mean of a dataset. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 333 | =HYPGEOM.DIST(num_successes, num_draws, successes_in_pop, pop_size) | See HYPGEOMDIST. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 334 | =HYPGEOMDIST(num_successes, num_draws, successes_in_pop, pop_size) | Calculates the probability of drawing a certain number of successes in a certain number of tries given a population of a certain size containing a certain number of successes, without replacement of draws. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 335 | =INTERCEPT(data_y, data_x) | Calculates the y-value at which the line resulting from linear regression of a dataset will intersect the y-axis (x=0). Learn more. | Statistical |
| 336 | =KURT(value1, value2) | Calculates the kurtosis of a dataset, which describes the shape, and in particular the 'peakedness' of that dataset. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 337 | =LARGE(data, n) | Returns the nth largest element from a data set, where n is user-defined. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 338 | =LOGINV(x, mean, standard_deviation) | Returns the value of the inverse log-normal cumulative distribution with given mean and standard deviation at a specified value. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 339 | =LOGNORM.DIST(x, mean, standard_deviation) | See LOGNORMDIST. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 340 | =LOGNORM.INV(x, mean, standard_deviation) | See LOGINV. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 341 | =LOGNORMDIST(x, mean, standard_deviation) | Returns the value of the log-normal cumulative distribution with given mean and standard deviation at a specified value. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 342 | =MAX(value1, [value2, ...]) | Returns the maximum value in a numeric dataset. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 343 | =MAXA(value1, value2) | Returns the maximum numeric value in a dataset. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 344 | =MAXIFS(range, criteria_range1, criterion1, [criteria_range2, criterion2], …) | Returns the maximum value in a range of cells, filtered by a set of criteria. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 345 | =MEDIAN(value1, [value2, ...]) | Returns the median value in a numeric dataset. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 346 | =MIN(value1, [value2, ...]) | Returns the minimum value in a numeric dataset. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 347 | =MINA(value1, value2) | Returns the minimum numeric value in a dataset. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 348 | =MINIFS(range, criteria_range1, criterion1, [criteria_range2, criterion2], …) | Returns the minimum value in a range of cells, filtered by a set of criteria. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 349 | =MODE(value1, [value2, ...]) | Returns the most commonly occurring value in a dataset. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 350 | =MODE.MULT(value1, value2) | Returns the most commonly occurring values in a dataset. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 351 | =MODE.SNGL(value1, [value2, ...]) | See MODE. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 352 | =NEGBINOM.DIST(num_failures, num_successes, prob_success) | See NEGBINOMDIST. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 353 | =NEGBINOMDIST(num_failures, num_successes, prob_success) | Calculates the probability of drawing a certain number of failures before a certain number of successes given a probability of success in independent trials. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 354 | =NORM.DIST(x, mean, standard_deviation, cumulative) | See NORMDIST. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 355 | =NORM.INV(x, mean, standard_deviation) | See NORMINV. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 356 | =NORM.S.DIST(x) | See NORMSDIST. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 357 | =NORM.S.INV(x) | See NORMSINV. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 358 | =NORMDIST(x, mean, standard_deviation, cumulative) | Returns the value of the normal distribution function (or normal cumulative distribution function) for a specified value, mean, and standard deviation. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 359 | =NORMINV(x, mean, standard_deviation) | Returns the value of the inverse normal distribution function for a specified value, mean, and standard deviation. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 360 | =NORMSDIST(x) | Returns the value of the standard normal cumulative distribution function for a specified value. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 361 | =NORMSINV(x) | Returns the value of the inverse standard normal distribution function for a specified value. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 362 | =PEARSON(data_y, data_x) | Calculates r, the Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient of a dataset. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 363 | =PERCENTILE(data, percentile) | Returns the value at a given percentile of a dataset. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 364 | =PERCENTILE.EXC(data, percentile) | Returns the value at a given percentile of a dataset, exclusive of 0 and 1. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 365 | =PERCENTILE.INC(data, percentile) | See PERCENTILE. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 366 | =PERCENTRANK(data, value, [significant_digits]) | Returns the percentage rank (percentile) of a specified value in a dataset. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 367 | =PERCENTRANK.EXC(data, value, [significant_digits]) | Returns the percentage rank (percentile) from 0 to 1 exclusive of a specified value in a dataset. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 368 | =PERCENTRANK.INC(data, value, [significant_digits]) | Returns the percentage rank (percentile) from 0 to 1 inclusive of a specified value in a dataset. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 369 | =PERMUTATIONA(number, number_chosen) | Returns the number of permutations for selecting a group of objects (with replacement) from a total number of objects. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 370 | =PERMUT(n, k) | Returns the number of ways to choose some number of objects from a pool of a given size of objects, considering order. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 371 | =PHI(x) | The PHI function returns the value of the normal distribution with mean 0 and standard deviation 1. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 372 | =POISSON(x, mean, cumulative) | See POISSON.DIST. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 373 | =POISSON.DIST(x, mean, [cumulative]) | Returns the value of the Poisson distribution function (or Poisson cumulative distribution function) for a specified value and mean. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 374 | =PROB(data, probabilities, low_limit, [high_limit]) | Given a set of values and corresponding probabilities, calculates the probability that a value chosen at random falls between two limits. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 375 | =QUARTILE(data, quartile_number) | Returns a value nearest to a specified quartile of a dataset. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 376 | =QUARTILE.EXC(data, quartile_number) | Returns value nearest to a given quartile of a dataset, exclusive of 0 and 4. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 377 | =QUARTILE.INC(data, quartile_number) | See QUARTILE. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 378 | =RANK(value, data, [is_ascending]) | Returns the rank of a specified value in a dataset. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 379 | =RANK.AVG(value, data, [is_ascending]) | Returns the rank of a specified value in a dataset. If there is more than one entry of the same value in the dataset, the average rank of the entries will be returned. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 380 | =RANK.EQ(value, data, [is_ascending]) | Returns the rank of a specified value in a dataset. If there is more than one entry of the same value in the dataset, the top rank of the entries will be returned. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 381 | =RSQ(data_y, data_x) | Calculates the square of r, the Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient of a dataset. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 382 | =SKEW(value1, value2) | Calculates the skewness of a dataset, which describes the symmetry of that dataset about the mean. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 383 | =SKEW.P(value1, value2) | Calculates the skewness of a dataset that represents the entire population. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 384 | =SLOPE(data_y, data_x) | Calculates the slope of the line resulting from linear regression of a dataset. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 385 | =SMALL(data, n) | Returns the nth smallest element from a data set, where n is user-defined. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 386 | =STANDARDIZE(value, mean, standard_deviation) | Calculates the normalized equivalent of a random variable given mean and standard deviation of the distribution. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 387 | =STDEV(value1, [value2, ...]) | Calculates the standard deviation based on a sample. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 388 | =STDEV.P(value1, [value2, ...]) | See STDEVP. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 389 | =STDEV.S(value1, [value2, ...]) | See STDEV. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 390 | =STDEVA(value1, value2) | Calculates the standard deviation based on a sample, setting text to the value `0`. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 391 | =STDEVP(value1, value2) | Calculates the standard deviation based on an entire population. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 392 | =STDEVPA(value1, value2) | Calculates the standard deviation based on an entire population, setting text to the value `0`. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 393 | =STEYX(data_y, data_x) | Calculates the standard error of the predicted y-value for each x in the regression of a dataset. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 394 | =T.DIST(x, degrees_freedom, cumulative) | Returns the right tailed Student distribution for a value x. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 395 | =T.DIST.2T(x, degrees_freedom) | Returns the two tailed Student distribution for a value x. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 396 | =T.DIST.RT(x, degrees_freedom) | Returns the right tailed Student distribution for a value x. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 397 | =T.INV(probability, degrees_freedom) | Calculates the negative inverse of the one-tailed TDIST function. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 398 | =T.INV.2T(probability, degrees_freedom) | Calculates the inverse of the two-tailed TDIST function. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 399 | =T.TEST(range1, range2, tails, type) | Returns the probability associated with St"udent's t-test. Determines whether two samples are likely to have come from the same two underlying populations that have the same mean. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 400 | =TDIST(x, degrees_freedom, tails) | Calculates the probability for Student's t-distribution with a given input (x). Learn more. | Statistical |
| 401 | =TINV(probability, degrees_freedom) | See T.INV.2T. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 402 | =TRIMMEAN(data, exclude_proportion) | Calculates the mean of a dataset excluding some proportion of data from the high and low ends of the dataset. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 403 | =TTEST(range1, range2, tails, type) | See T.TEST. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 404 | =VAR(value1, [value2, ...]) | Calculates the variance based on a sample. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 405 | =VAR.P(value1, [value2, ...]) | See VARP. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 406 | =VAR.S(value1, [value2, ...]) | See VAR. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 407 | =VARA(value1, value2) | Calculates an estimate of variance based on a sample, setting text to the value `0`. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 408 | =VARP(value1, value2) | Calculates the variance based on an entire population. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 409 | =VARPA(value1, value2, ...) | Calculates the variance based on an entire population, setting text to the value `0`. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 410 | =WEIBULL(x, shape, scale, cumulative) | Returns the value of the Weibull distribution function (or Weibull cumulative distribution function) for a specified shape and scale. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 411 | =WEIBULL.DIST(x, shape, scale, cumulative) | See WEIBULL. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 412 | =Z.TEST(data, value, [standard_deviation]) | Returns the one-tailed P-value of a Z-test with standard distribution. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 413 | =ZTEST(data, value, [standard_deviation]) | See Z.TEST. Learn more. | Statistical |
| 414 | =ARABIC(roman_numeral) | Computes the value of a Roman numeral. Learn more. | Text |
| 415 | =ASC(text) | Converts full-width ASCII and katakana characters to their half-width counterparts. All standard-width characters will remain unchanged. Learn more. | Text |
| 416 | =CHAR(table_number) | Convert a number into a character according to the current Unicode table. Learn more. | Text |
| 417 | =CLEAN(text) | Returns the text with the non-printable ASCII characters removed. Learn more. | Text |
| 418 | =CODE(string) | Returns the numeric Unicode map value of the first character in the string provided. Learn more. | Text |
| 419 | =CONCATENATE(string1, [string2, ...]) | Appends strings to one another. Learn more. | Text |
| 420 | =DOLLAR(number, [number_of_places]) | Formats a number into the locale-specific currency format. Learn more. | Text |
| 421 | =EXACT(string1, string2) | Tests whether two strings are identical. Learn more. | Text |
| 422 | =FIND(search_for, text_to_search, [starting_at]) | Returns the position at which a string is first found within text. Learn more. | Text |
| 423 | =FINDB(search_for, text_to_search, [starting_at]) | Returns the position at which a string is first found within text counting each double-character as 2. Learn more. | Text |
| 424 | =FIXED(number, [number_of_places], [suppress_separator]) | Formats a number with a fixed number of decimal places. Learn more. | Text |
| 425 | =JOIN(delimiter, value_or_array1, [value_or_array2, ...]) | Concatenates the elements of one or more one-dimensional arrays using a specified delimiter. Learn more. | Text |
| 426 | =LEFT(string, [number_of_characters]) | Returns a substring from the beginning of a specified string. Learn more. | Text |
| 427 | =LEFTB(string, num_of_bytes) | Returns the left portion of a string up to a certain number of bytes. Learn more. | Text |
| 428 | =LEN(text) | Returns the length of a string. Learn more. | Text |
| 429 | =LENB(string) | Returns the length of a string in bytes.'. Learn more. | Text |
| 430 | =LOWER(text) | Converts a specified string to lowercase. Learn more. | Text |
| 431 | =MID(string, starting_at, extract_length) | Returns a segment of a string. Learn more. | Text |
| 432 | =MIDB(string) | Returns a section of a string starting at a given character and up to a specified number of bytes. Learn more. | Text |
| 433 | =PROPER(text_to_capitalize) | Capitalizes each word in a specified string. Learn more. | Text |
| 434 | =REGEXEXTRACT(text, regular_expression) | Extracts matching substrings according to a regular expression. Learn more. | Text |
| 435 | =REGEXMATCH(text, regular_expression) | Whether a piece of text matches a regular expression. Learn more. | Text |
| 436 | =REGEXREPLACE(text, regular_expression, replacement) | Replaces part of a text string with a different text string using regular expressions. Learn more. | Text |
| 437 | =REPLACE(text, position, length, new_text) | Replaces part of a text string with a different text string. Learn more. | Text |
| 438 | =REPLACEB(text, position, num_bytes, new_text) | Replaces part of a text string, based on a number of bytes, with a different text string. Learn more. | Text |
| 439 | =REPT(text_to_repeat, number_of_repetitions) | Returns specified text repeated a number of times. Learn more. | Text |
| 440 | =RIGHT(string, [number_of_characters]) | Returns a substring from the end of a specified string. Learn more. | Text |
| 441 | =RIGHTB(string, num_of_bytes) | Returns the right portion of a string up to a certain number of bytes. Learn more. | Text |
| 442 | =ROMAN(number, [rule_relaxation]) | Formats a number in Roman numerals. Learn more. | Text |
| 443 | =SEARCH(search_for, text_to_search, [starting_at]) | Returns the position at which a string is first found within text. Learn more. | Text |
| 444 | =SEARCHB(search_for, text_to_search, [starting_at]) | Returns the position at which a string is first found within text counting each double-character as 2. Learn more. | Text |
| 445 | =SPLIT(text, delimiter, [split_by_each], [remove_empty_text]) | Divides text around a specified character or string, and puts each fragment into a separate cell in the row. Learn more. | Text |
| 446 | =SUBSTITUTE(text_to_search, search_for, replace_with, [occurrence_number]) | Replaces existing text with new text in a string. Learn more. | Text |
| 447 | =T(value) | Returns string arguments as text. Learn more. | Text |
| 448 | =TEXT(number, format) | Converts a number into text according to a specified format. Learn more. | Text |
| 449 | =TEXTJOIN(delimiter, ignore_empty, text1, [text2], …) | Combines the text from multiple strings and/or arrays, with a specifiable delimiter separating the different texts. Learn more. | Text |
| 450 | =TRIM(text) | Removes leading and trailing spaces in a specified string. Learn more. | Text |
| 451 | =UNICHAR(number) | Returns the Unicode character for a number. Learn more. | Text |
| 452 | =UNICODE(text) | Returns the decimal Unicode value of the first character of the text. Learn more. | Text |
| 453 | =UPPER(text) | Converts a specified string to uppercase. Learn more. | Text |
| 454 | =VALUE(text) | Converts a string in any of the date, time or number formats that Google Sheets understands into a number. Learn more. | Text |
| 455 | =DAVERAGE(database, field, criteria) | Returns the average of a set of values selected from a database table-like array or range using a SQL-like query. Learn more. | Database |
| 456 | =DCOUNT(database, field, criteria) | Counts numeric values selected from a database table-like array or range using a SQL-like query. Learn more. | Database |
| 457 | =DCOUNTA(database, field, criteria) | Counts values, including text, selected from a database table-like array or range using a SQL-like query. Learn more. | Database |
| 458 | =DGET(database, field, criteria) | Returns a single value from a database table-like array or range using a SQL-like query. Learn more. | Database |
| 459 | =DMAX(database, field, criteria) | Returns the maximum value selected from a database table-like array or range using a SQL-like query. Learn more. | Database |
| 460 | =DMIN(database, field, criteria) | Returns the minimum value selected from a database table-like array or range using a SQL-like query. Learn more. | Database |
| 461 | =DPRODUCT(database, field, criteria) | Returns the product of values selected from a database table-like array or range using a SQL-like query. Learn more. | Database |
| 462 | =DSTDEV(database, field, criteria) | Returns the standard deviation of a population sample selected from a database table-like array or range using a SQL-like query. Learn more. | Database |
| 463 | =DSTDEVP(database, field, criteria) | Returns the standard deviation of an entire population selected from a database table-like array or range using a SQL-like query. Learn more. | Database |
| 464 | =DSUM(database, field, criteria) | Returns the sum of values selected from a database table-like array or range using a SQL-like query. Learn more. | Database |
| 465 | =DVAR(database, field, criteria) | Returns the variance of a population sample selected from a database table-like array or range using a SQL-like query. Learn more. | Database |
| 466 | =DVARP(database, field, criteria) | Returns the variance of an entire population selected from a database table-like array or range using a SQL-like query. Learn more. | Database |
| 467 | =CONVERT(value, start_unit, end_unit) | Converts a numeric value to a different unit of measure. Learn more. | Parser |
| 468 | =TO_DATE(value) | Converts a provided number to a date. Learn more. | Parser |
| 469 | =TO_DOLLARS(value) | Converts a provided number to a dollar value. Learn more. | Parser |
| 470 | =TO_PERCENT(value) | Converts a provided number to a percentage. Learn more. | Parser |
| 471 | =TO_PURE_NUMBER(value) | Converts a provided date/time, percentage, currency or other formatted numeric value to a pure number without formatting. Learn more. | Parser |
| 472 | =TO_TEXT(value) | Converts a provided numeric value to a text value. Learn more. | Parser |
| 473 | =ARRAY_CONSTRAIN(input_range, num_rows, num_cols) | Constrains an array result to a specified size. Learn more. | Array |
| 474 | =FLATTEN(range1, [range2,...]) | Flattens all the values from one or more ranges into a single column. Learn more. | Array |
| 475 | =FREQUENCY(data, classes) | Calculates the frequency distribution of a one-column array into specified classes. Learn more. | Array |
| 476 | =GROWTH(known_data_y, [known_data_x], [new_data_x], [b]) | Given partial data about an exponential growth trend, fits an ideal exponential growth trend and/or predicts further values. Learn more. | Array |
| 477 | =LINEST(known_data_y, [known_data_x], [calculate_b], [verbose]) | Given partial data about a linear trend, calculates various parameters about the ideal linear trend using the least-squares method. Learn more. | Array |
| 478 | =LOGEST(known_data_y, [known_data_x], [b], [verbose]) | Given partial data about an exponential growth curve, calculates various parameters about the best fit ideal exponential growth curve. Learn more. | Array |
| 479 | =MDETERM(square_matrix) | Returns the matrix determinant of a square matrix specified as an array or range. Learn more. | Array |
| 480 | =MINVERSE(square_matrix) | Returns the multiplicative inverse of a square matrix specified as an array or range. Learn more. | Array |
| 481 | =MMULT(matrix1, matrix2) | Calculates the matrix product of two matrices specified as arrays or ranges. Learn more. | Array |
| 482 | =SUMPRODUCT(array1, [array2, ...]) | Calculates the sum of the products of corresponding entries in two equal-sized arrays or ranges. Learn more. | Array |
| 483 | =SUMX2MY2(array_x, array_y) | Calculates the sum of the differences of the squares of values in two arrays. Learn more. | Array |
| 484 | =SUMX2PY2(array_x, array_y) | Calculates the sum of the sums of the squares of values in two arrays. Learn more. | Array |
| 485 | =SUMXMY2(array_x, array_y) | Calculates the sum of the squares of differences of values in two arrays. Learn more. | Array |
| 486 | =TRANSPOSE(array_or_range) | Transposes the rows and columns of an array or range of cells. Learn more. | Array |
| 487 | =TREND(known_data_y, [known_data_x], [new_data_x], [b]) | Given partial data about a linear trend, fits an ideal linear trend using the least squares method and/or predicts further values. Learn more. | Array |
| 488 | =ENCODEURL(text) | Encodes a string of text for the purpose of using in a URL query. Learn more. | Web |
| 489 | =HYPERLINK(url, [link_label]) | Creates a hyperlink inside a cell. Learn more. | Web |
| 490 | =IMPORTDATA(url) | Imports data at a given url in .csv (comma-separated value) or .tsv (tab-separated value) format. Learn more. | Web |
| 491 | =IMPORTFEED(url, [query], [headers], [num_items]) | Imports a RSS or ATOM feed. Learn more. | Web |
| 492 | =IMPORTHTML(url, query, index) | Imports data from a table or list within an HTML page. Learn more. | Web |
| 493 | =IMPORTRANGE(spreadsheet_url, range_string) | Imports a range of cells from a specified spreadsheet. Learn more. | Web |
| 494 | =IMPORTXML(url, xpath_query) | Imports data from any of various structured data types including XML, HTML, CSV, TSV, and RSS and ATOM XML feeds. Learn more. | Web |
| 495 | =ISURL(value) | Checks whether a value is a valid URL. Learn more. | Web |
This page contains modified content from "Google Sheets function list" available here.
That content is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 2.0 because it is an adaptation of a work licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License, version 2.0 or later.
I have made modifications to function syntax and coloring to better reflect their use within Google Sheets and the table's formatting.
As listed in the "Google Sheets function list", it contains modified content from Appendix B of the OpenOffice.org "Calc Guide".
The original "Calc Guide" content is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 2.0.
The copyright notice found in the OpenOffice.org "Calc Guide" is included in its complete form below:
Copyright
This document is Copyright © 2005 by its contributors as listed in the section titled Authors. You can distribute it and/or modify it under the terms of either the GNU General Public License, version 2 or later, or the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 2.0 or later.
All trademarks within this guide belong to their legitimate owners.
Authors
- Magnus Adielsson
- Richard Barnes
- Peter Kupfer
- Iain Roberts
- Jean Hollis Weber
Want Better-Looking Google Sheets?
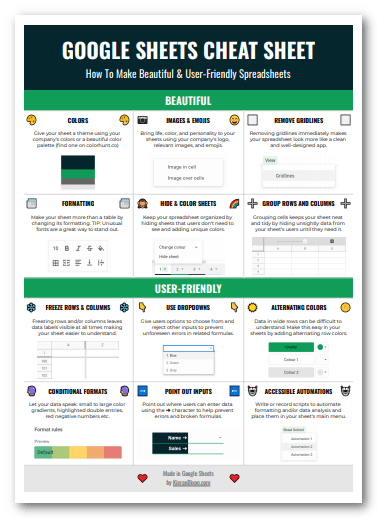
Get my 12-tip cheat sheet that will make your spreadsheets more user-friendly.
You'll get updates from me with an easy-to-find "unsubscribe" link.